Regulatory Compliance Examples: 5 Illustrative Case Studies
By Emily Fenton
Updated February 27, 2023

Regulatory Compliance Examples: 5 Important Regulatory Frameworks
A regulatory framework is a model used for proposing, enacting and reforming regulations in an effective and logical way. Policymakers develop frameworks in a specific area of interest, or use a current framework to work on a new regulatory project.
Regulatory frameworks help protect consumers, and ensure businesses are run properly. But even if you’re dedicated to ensuring your company follows all regulatory frameworks to the letter, keeping up with every regulatory change likely feels futile.
Visualping can be a lifesaver. This easy-to-use yet powerful tool that lets you monitor any web page with AI, including government and regulatory websites, so you don't have to.
When a change is detected, you get an email alert, with an AI-generated summary of the page change, distilled in 2 to 3 lines. The alert also includes a screenshot of the page, with the changes highlighted, for you to view.
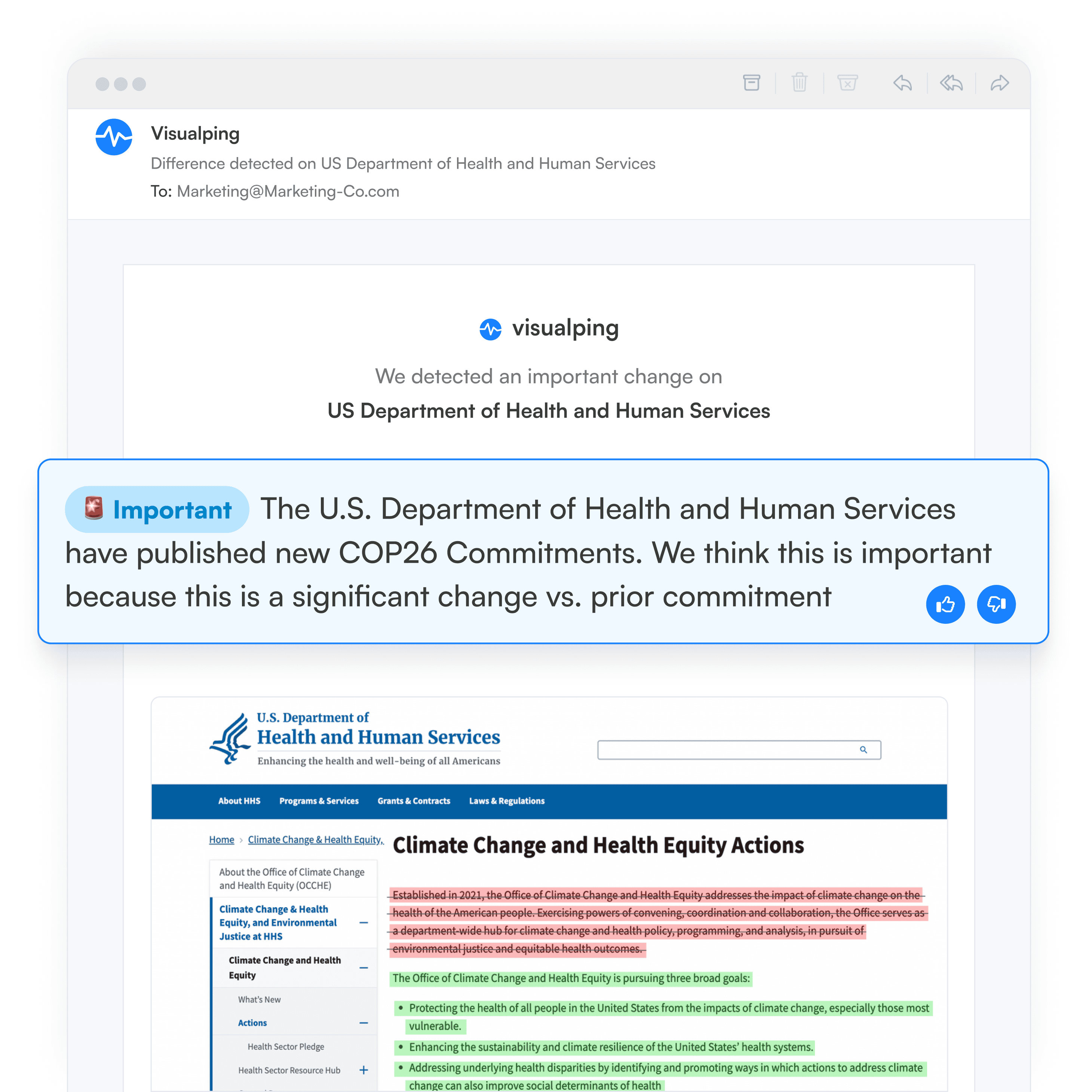
You can use Visualping to follow all relevant legislative activity, and subsequent regulatory updates, to keep your company running smoothly and violation-free. Here are some major regulatory compliance examples your company may need to track.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) law was enacted in the European Union in May 2018. It's a privacy law that outlines safety standards for storing user or customer details online. Those details include an individual user’s IP address, device ID, home address, etc.
It impacts all companies conducting business in Europe. Even if your company isn’t based in the E.U., you’re still legally bound by the GDPR regarding European users’ information.
GDPR Regulatory Updates
GDPR is not set in stone — it hasn’t actually stood still since it took effect in 2018. The E.U. updates the GDPR with key developments that evolve over time, and which impact companies inside and outside the EU.
One example goes back to May 2020, when the E.U. updated its GDPR guidance to clarify several points, such as on the use of cookie walls: the GDPR clarified that cookie walls do not offer users a genuine choice, and so they can't be used as a formal request for user data. Nor does scrolling or swiping through ewb content equate to implied consent -- the E.U. reiterated that consent must be explicit.
Changes to GDPR happen all the time and, if they impact your business, then you'll need to know. In order to companies to stay compliant, then monitoring GDPR for updates is critical in limiting compliance risk.
Even accidental oversights can result in companies facing steep fines for GDPR violations. In fact, by early 2021, the E.U. had already assessed more than $332 million in fines!
When a business is facing a GDPR fine, ten factors are used to determine the amount:
- How serious is the violation?
- Was it an intentional violation or due to negligence?
- Did the organization immediately take action to correct the mistake?
- Did the organization have precautionary measures in place to prevent GDPR violations (like clear compliance regulations)?
- Is there a history of noncompliance?
- Did the organization cooperate with authorities?
- How sensitive is the affected data?
- Did the organization notify authorities of the violation on its own?
- Does the organization already have GDPR certifications?
- Are there other mitigating or aggravating factors to be considered?
Since expectations of the GDPR are subject to change over time, and considering even accidental violations can have serious consequences, it’s imperative to monitor regulatory changes from frameworks like the GDPR and CCPA, and others like it.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
In the age of big data, businesses are collecting more and more information on their consumers. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), a law that went into effect in January 2020, helps consumers understand and control the data about them that are being collected.
Under the CCPA, consumers have the right to know what data a given company collects and remove any publicly posted information. Perhaps most importantly, consumers can also opt out of having their personal information shared or sold. The law prohibits businesses from discriminating against customers who opt out.
Unlike GDPR, the CCPA only applies to commercial companies:
- Who process the data of more than 50,000 California residents a year, OR
- Who generate gross revenue of more than $25m a year, OR
- Who make more than half of their annual revenue from selling California residents’ personal data
CCPA Regulatory Updates
Like the GDPR, the CCPA is also subject to change over time. The designated regulator for enforcing the CCPA issued a notice of new regulations in July 2022, to take effect Jan. 2023. While these changes reflected incremental amendments to the existing CCPA, the updates still significantly impacted the handling of information for some companies.
For example, new regulations for data minimization required that the “collection, use, retention, and/or sharing" of private consumer data should only be "reasonably necessary and proportionate to achieve the purpose(s) for which the personal information was collected or processed.” It goes further to define “necessary and proportionate” in this context as being “what an average consumer would expect” at the time of collection.
The CCPA also gives consumers recourse in the event of a data breach or unlawful sale of information.
If the stolen or leaked data includes Social Security numbers, government-issued ID numbers, financial account numbers, HIPAA-protected health information, or biometric data, consumers may bring a lawsuit against the company that failed to protect the data.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
It’s all too easy for hackers to steal sensitive data if credit and debit card numbers aren’t adequately protected online.
Much like banking regulatory compliance standards, there’s also a regulatory compliance framework for online merchants. The PCI DSS aims to ensure that every company that accepts online card payments processes and stores data securely.
To comply with the law, these companies must use a PCI-compliant provider to store and handle payment data. A PCI-compliant provider follows these 12 critical guidelines:
- Have a working firewall
- Change any default passwords or security settings
- Protect all stored data
- Encrypt data if it’s being transmitted via a public network
- Maintain working antivirus software
- Have clear security systems and processes to address vulnerabilities
- Restrict access to customer data to only employees who need to know
- Give every employee with computer access a unique ID
- Limit any kind of physical access to customer data
- Track who accesses customer data
- Conduct regular process and system testing
- Have a set, written policy for information security
The PCI DSS isn’t a law. However, payment and merchant service providers often require businesses to be PCI-compliant as part of their contracts. If a business becomes noncompliant, it may face considerable fines.
If you handle any type of online payment, you’ll need to make sure your internal regulatory compliance policy is in line with PCI DSS.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is probably one of the best-known compliance frameworks. It’s designed to protect data collected in healthcare and medical settings. For businesses in the healthcare sector, maintaining HIPAA compliance is vitally important.
Most healthcare data is stored electronically, and part of HIPAA compliance is protecting electronically-stored data from would-be hackers.
If your business is in the healthcare industry, you should have a robust data protection protocol and confirm that you’re fully compliant with any IT security guidelines. Make sure you have a compliance monitoring guide covering hard copies and electronic data.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
First introduced in 2002, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act is one of the oldest regulatory frameworks in existence. It was passed to help prevent financial fraud by corporations. It accomplished this by strengthening regulations on transparency in corporate accounting and implementing new regulatory and compliance requirements.
One key aspect of SOX is that it establishes standards to ensure that external auditors have no conflicts of interest with the company being audited. The law also requires all public businesses to store records and messages for at least five years.
How to Use Visualping to Keep on Top of Legislative and Regulatory Changes
Not all of the above examples will apply to your business. But once you’ve gathered a list of websites you do need to monitor, you can get started using Visualping. Here’s a quick guide.
Step 1: Copy the URL of the Law or Regulation from Where It’s Published Online, Then Paste It into the Search Field on Visualping’s Homepage
This part is important, as you want to be sure you’re following the right webpage. Copying and pasting directly is the best way to avoid URL errors.
Step 2: Select the Part of the Page You Want Visualping to Monitor for Changes
Use your cursor to select the area of the page you want to monitor for changes. For example, if you’re using monitoring tools for law firms, you might highlight a portion of the state or local code to follow. You also can select whether you want Visualping to look for changes in the text, visual elements, or both.
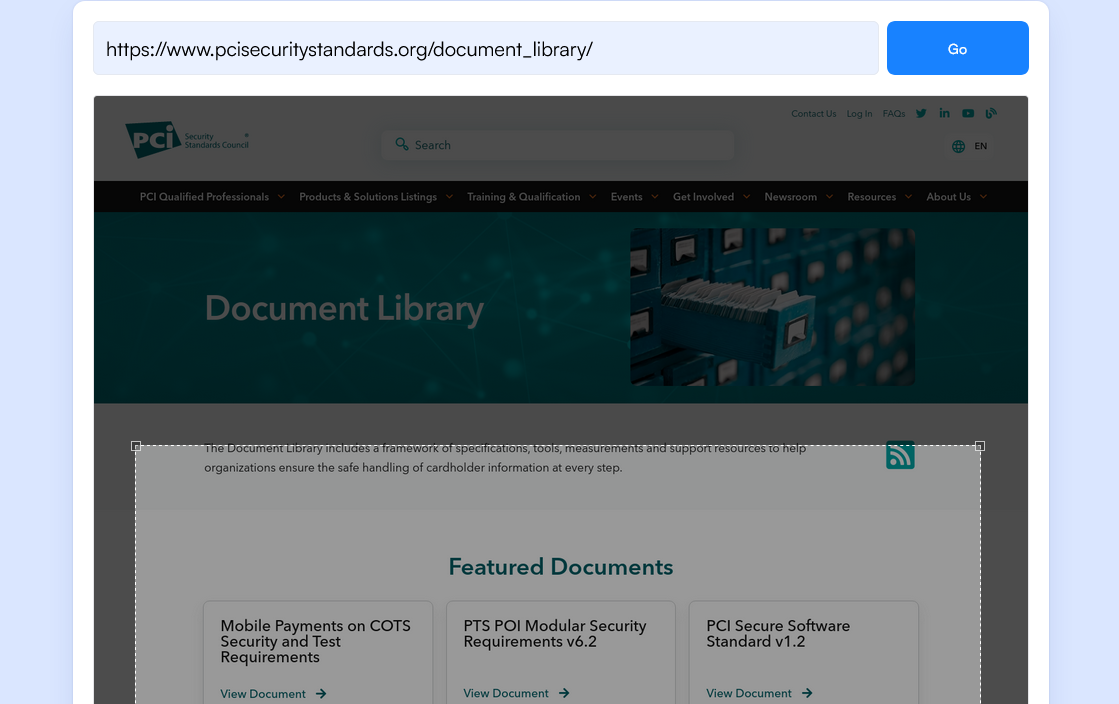
Step 3: Choose the Frequency of Monitoring
Next, decide how often you want the platform to scan your website of choice. You can have Visualping perform daily, weekly, or monthly checks with a free plan. With an upgraded plan, you can have the platform run a scan as often as every five minutes.
Step 4: Enter the Email Address Where You Want to Receive Alerts
Make sure you provide an email address you check regularly. That way, you’ll be able to take action quickly if there’s a major regulatory change.
Step 5: Check Your Email to Complete the Signup Process
Once you’ve linked your email to Visualping, all you need to do is click the confirmation link in the automatically generated email you receive and you’ll be ready to go!
Keep Track of Regulatory Compliance Standards with Visualping
With Visualping, you can be confident that you’ll know about crucial regulatory changes as soon as they happen. Whether you’re keeping up with the rigors of pharmaceutical regulatory compliance, tracking legislation changes in the financial sector, or staying current on something else, we can help.
Visualping is simple and intuitive, and you can get started in minutes. Try it today for free!
Want to monitor web changes that impact your business?
Sign up with Visualping to get alerted of important updates, from anywhere online.
Emily Fenton
Emily is the Product Marketing Manager at Visualping. She has a degree in English Literature and a Masters in Management. When she’s not researching and writing about all things Visualping, she loves exploring new restaurants, playing guitar and petting her cats.